四个层级
根据数据平面和控制平面分离的原则,Milvus 由四个层级组成,在可扩展性和灾难恢复方面相互独立。
访问层
由一组无状态代理组成,访问层是系统的前端层,也是用户的终端。它验证客户端请求并减少返回结果:
- 代理本身是无状态的。它使用负载平衡组件(例如 Nginx、Kubernetes Ingress、NodePort 和 LVS)提供一个统一的服务地址。
- 由于 Milvus 采用了大规模并行处理(MPP)架构,代理在将最终结果返回给客户端之前,会聚合和后处理中间结果。
协调服务
协调服务负责分配任务给工作节点,并作为系统的大脑。它承担的任务包括集群拓扑管理、负载均衡、时间戳生成、数据声明和数据管理。
有四种协调员类型:根协调员(root coord)、数据协调员(data coord)、查询协调员(query coord)和索引协调员(index coord)。
Root coordinator (root coord)
Root coord handles data definition language (DDL) and data control language (DCL) requests, such as create or delete collections, partitions, or indexes, as well as manage TSO (timestamp Oracle) and time ticker issuing.
查询协调器(查询协调器)
查询协调器负责查询节点的拓扑结构和负载均衡,以及从正在增长的段到密封的段的交接。
Data coordinator (data coord)
Data coord manages topology of the data nodes, maintains metadata, and triggers flush, compact, and other background data operations.
索引协调器(index coord)
索引协调器管理索引节点的拓扑结构,构建索引,并维护索引元数据。
Worker nodes
The arms and legs. Worker nodes are dumb executors that follow instructions from the coordinator service and execute data manipulation language (DML) commands from the proxy. Worker nodes are stateless thanks to separation of storage and computation, and can facilitate system scale-out and disaster recovery when deployed on Kubenetes. There are three types of worker nodes:
查询节点
查询节点通过订阅日志代理程序检索增量日志数据并将其转换为不断增长的段,从对象存储中加载历史数据,并在向量和标量数据之间运行混合搜索。
Data node
Data node retrieves incremental log data by subscribing to the log broker, processes mutation requests, and packs log data into log snapshots and stores them in the object storage.
索引节点
索引节点用于建立索引。索引节点不需要常驻内存,可以使用无服务器框架实现。
Storage
Storage is the bone of the system, responsible for data persistence. It comprises meta storage, log broker, and object storage.
Meta storage
Meta storage stores snapshots of metadata such as collection schema, node status, and message consumption checkpoints. Storing metadata demands extremely high availability, strong consistency, and transaction support, so Milvus chose etcd for meta store. Milvus also uses etcd for service registration and health check.
对象存储
对象存储存储日志的快照文件、标量和矢量数据的索引文件以及中间查询结果。Milvus 使用 MinIO 作为对象存储,可以轻松部署在 AWS S3 和 Azure Blob 两个世界上最受欢迎、最具成本效益的存储服务上。但是,对象存储具有高访问延迟并按查询数量收费。为了提高其性能并降低成本,Milvus 计划在基于内存或 SSD 的缓存池上实现冷热数据分离。
日志代理
日志代理是支持回放的发布-订阅系统,负责流数据持久化,执行可靠异步查询,事件通知以及返回查询结果。它还确保工作节点从系统崩溃中恢复时的增量数据的完整性。Milvus集群使用Pulsar作为日志代理;Milvus独立版使用RocksDB作为日志代理。此外,日志代理可以轻松替换为流数据存储平台,如Kafka和Pravega。
Milvus is built around log broker and follows the "log as data" principle, so Milvus does not maintain a physical table but guarantees data reliability through logging persistence and snapshot logs.
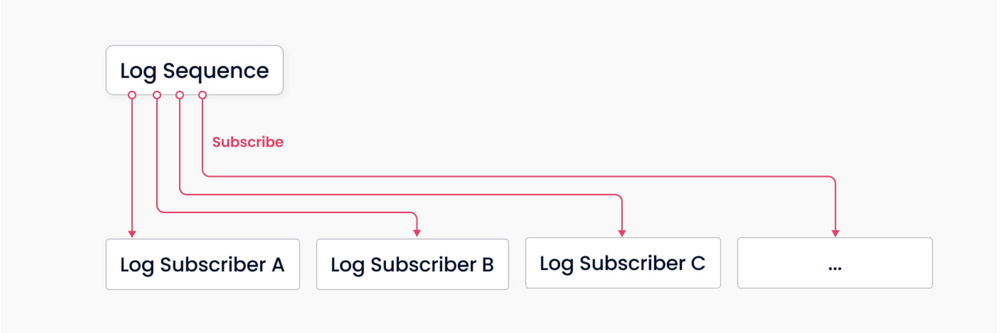
Log mechanism.
The log broker is the backbone of Milvus. It is responsible for data persistence and read-write disaggregation, thanks to its innate pub-sub mechanism. The above illustration shows a simplified depiction of the mechanism, where the system is divided into two roles, log broker (for maintaining the log sequence) and log subscriber. The former records all operations that change collection states; the latter subscribes to the log sequence to update the local data and provides services in the form of read-only copies. The pub-sub mechanism also makes room for system extendability in terms of change data capture (CDC) and globally-distributed deployment.
What's next
- 阅读主要组件以获取更多关于Milvus架构的详细信息。