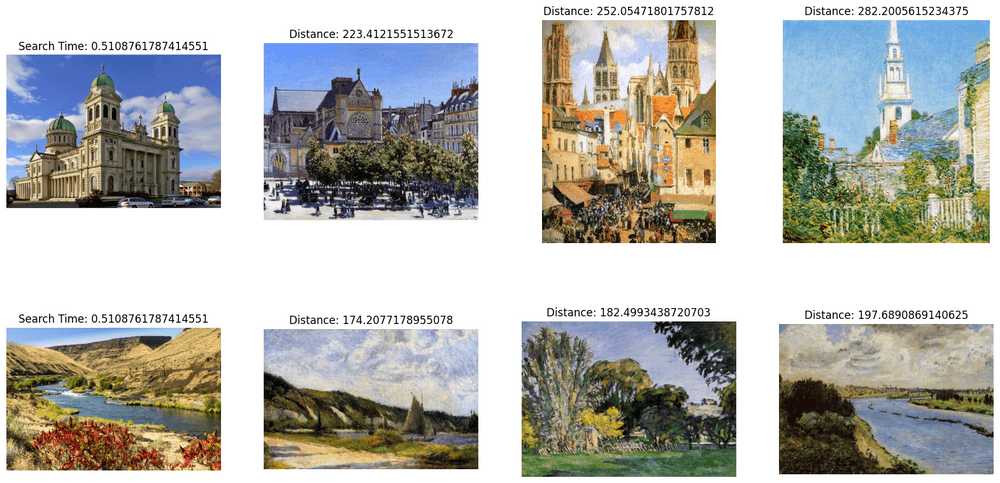图像搜索示例
在本页中,我们将通过使用Milvus进行简单的图像搜索示例。我们搜索的数据集是在Kaggle (opens in a new tab)上找到的印象派分类器数据集。对于本示例,我们已在公共谷歌驱动器上重新托管了数据。
对于这个示例,我们只是使用了Torchvision预训练的Resnet50模型来进行嵌入。让我们开始吧!
安装依赖包
对于这个例子,我们将使用pymilvus 来连接和使用Milvus,torch来运行嵌入模型, torchvision来构建实际模型和预处理,gdown 用来下载示例数据集,tqdm用于进度条。
pip install pymilvus torch gdown torchvision tqdm获取数据
我们将使用gdown 从Google Drive获取zip文件,然后使用内置的zipfile库进行解压缩。
import gdown
import zipfile
url = 'https://drive.google.com/uc?id=1OYDHLEy992qu5C4C8HV5uDIkOWRTAR1_'
output = './paintings.zip'
gdown.download(url, output)
with zipfile.ZipFile("./paintings.zip","r") as zip_ref:
zip_ref.extractall("./paintings")数据集的大小为2.35 GB,下载所需的时间取决于您的网络状况。
全局变量
这些是我们将使用的一些主要全局变量,以便于跟踪和更新。
# Milvus Setup Arguments
COLLECTION_NAME = 'image_search' # 集合名称
DIMENSION = 2048 # 在这个例子中嵌入向量的大小
MILVUS_HOST = "localhost"
MILVUS_PORT = "19530"
# Inference Arguments
BATCH_SIZE = 128
TOP_K = 3设置Milvus
在此,我们将开始设置Milvus。步骤如下:
- 使用提供的 URI 连接到 Milvus 实例。
from pymilvus import connections
# 连接到实例
connections.connect(host=MILVUS_HOST, port=MILVUS_PORT)- 如果集合已经存在,则删除它。
from pymilvus import utility
# 删除具有相同名称的以前集合
if utility.has_collection(COLLECTION_NAME):
utility.drop_collection(COLLECTION_NAME)- 创建包含 ID、图像文件路径和其嵌入的集合。
from pymilvus import FieldSchema, CollectionSchema, DataType, Collection
# 创建包含 ID、图像文件路径和图像嵌入的集合
fields = [
FieldSchema(name='id', dtype=DataType.INT64, is_primary=True, auto_id=True),
FieldSchema(name='filepath', dtype=DataType.VARCHAR, max_length=200), # VARCHAR 需要一个最大长度,所以为了这个例子,它们被设置为200个字符。
FieldSchema(name='image_embedding', dtype=DataType.FLOAT_VECTOR, dim=DIMENSION)
]
schema = CollectionSchema(fields=fields)
collection = Collection(name=COLLECTION_NAME, schema=schema)- 为新创建的集合创建索引并将其加载到内存中。
#为集合创建AutoIndex索引
index_params = {
'metric_type':'L2',
'index_type':"IVF_FLAT",
'params':{'nlist': 16384}
}
collection.create_index(field_name="image_embedding", index_params=index_params)
collection.load()一旦完成这些步骤,集合就可以被插入和搜索。添加的任何数据都会被自动索引,并立即可用于搜索。如果数据非常新鲜,则搜索可能会较慢,因为在仍在索引过程中的数据上将使用暴力搜索。
插入数据
在本示例中,我们将使用由 torch提供的ResNet50模型及其模型库。为了获取嵌入,我们去掉了最终的分类层,从而使模型提供了2048维的嵌入。torch上的所有Vision模型都使用我们在这里包含的相同预处理。
在接下来的几个步骤中,我们将数据插入Milvus后,我们可以开始执行搜索。
在本例中,我们将搜索两个示例图像。因为我们正在进行批量搜索,所以搜索时间将在批次图像之间共享。
import glob
# Get the filepaths of the search images
search_paths = glob.glob('./paintings/test_paintings/**/*.jpg', recursive=True)
len(search_paths)
import time
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
# Embed the search images
def embed(data):
with torch.no_grad():
ret = model(torch.stack(data))
# If more than one image, use squeeze
if len(ret) > 1:
return ret.squeeze().tolist()
# Squeeze would remove batch for single image, so using flatten
else:
return torch.flatten(ret, start_dim=1).tolist()
data_batch = [[],[]]
for path in search_paths:
im = Image.open(path).convert('RGB')
data_batch[0].append(preprocess(im))
data_batch[1].append(path)
embeds = embed(data_batch[0])
start = time.time()
res = collection.search(embeds, anns_field='image_embedding', param={'nprobe': 128}, limit=TOP_K, output_fields=['filepath'])
finish = time.time()
# Show the image results
f, axarr = plt.subplots(len(data_batch[1]), TOP_K + 1, figsize=(20, 10), squeeze=False)
for hits_i, hits in enumerate(res):
axarr[hits_i][0].imshow(Image.open(data_batch[1][hits_i]))
axarr[hits_i][0].set_axis_off()
axarr[hits_i][0].set_title('Search Time: ' + str(finish - start))
for hit_i, hit in enumerate(hits):
axarr[hits_i][hit_i + 1].imshow(Image.open(hit.entity.get('filepath')))
axarr[hits_i][hit_i + 1].set_axis_off()
axarr[hits_i][hit_i + 1].set_title('Distance: ' + str(hit.distance))
# Save the search result in a separate image file alongside your script.
plt.savefig('search_result.png')
搜索结果图像应该类似于以下内容: