相似度度量
在Milvus中,相似度度量用于衡量向量之间的相似性。选择一个好的距离度量方法可以显著提高分类和聚类的性能。
下表显示了这些广泛使用的相似度度量方法与各种输入数据形式和Milvus索引的匹配情况。
| Similarity Metrics | Index Types |
|---|---|
| * 欧几里得距离(L2) |
- 内积(IP) | * FLAT
- IVF_FLAT
- IVF_SQ8
- IVF_PQ
- HNSW
- 烦扰
- DISKANN |
| Distance Metrics | Index Types |
|---|---|
| * Jaccard |
- Tanimoto
- Hamming | * BIN_FLAT
- BIN_IVF_FLAT | | * 超结构
- 子结构 | * BIN_FLAT |
欧几里得距离(L2)
实际上,欧几里得距离测量连接两点的线段的长度。
欧几里得距离的公式如下:
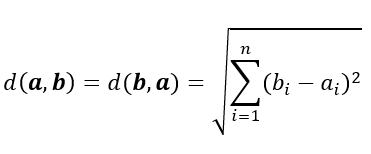
Euclidean distance.
其中a =(a1,a2,...,an)和b =(b1,b2,...,bn)是n维欧几里得空间中的两个点
它是最常用的距离度量方法,在数据连续时非常有用。
Milvus only caculates the value before applying square root when Euclidean distance is chosen as the distance metric.
内积 (IP)
两个嵌入之间的IP距离定义如下:
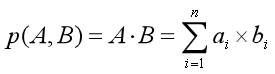
Inner product.
其中A和B是嵌入,||A||和||B||是A和B的范数。
如果您更关心向量的方向而不是大小,那么IP更有用。
If you use IP to calculate embeddings similarities, you must normalize your embeddings. After normalization, the inner product equals cosine similarity.
假设X'是从嵌入X中归一化的:
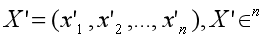
Normalize.
两个嵌入之间的相关性如下:
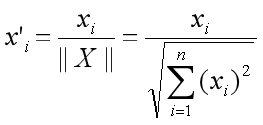
Normalization.
Jaccard距离
Jaccard相似系数测量两个样本集之间的相似性,定义为所定义集合的交集的基数除以它们的并集的基数。它仅适用于有限的样本集。
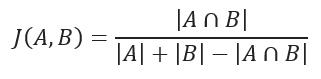
Jaccard similarity coefficient.
Jaccard距离测量数据集之间的不相似度,是通过从1中减去Jaccard相似系数得到的。对于二进制变量,Jaccard距离等同于Tanimoto系数。
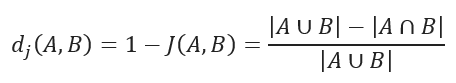
Jaccard distance.
Tanimoto距离
对于二进制变量,Tanimoto系数等同于Jaccard距离:
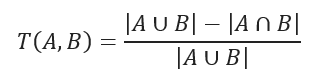
Tanimoto coefficient.
在Milvus中,Tanimoto系数仅适用于二进制变量,对于二进制变量,Tanimoto系数范围从0到+1(+1表示最高相似度)。
对于二进制变量,Tanimoto距离的公式为:
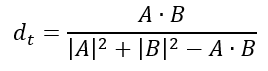
Tanimoto distance.
该值的范围是从0到+无穷大。
海明距离
海明距离是用来度量二进制数据字符串的。两个等长字符串之间的海明距离是它们在相应位置上不同的二进制位数。
例如,假设有两个字符串,1101 1001 和 1001 1101。
11011001 ⊕ 10011101 = 01000100。由于其中包含两个1,所以(11011001, 10011101)的海明距离d = 2。
Superstructure
超结构用于衡量化学结构和其超结构的相似性。当值等于0时,这意味着数据库中的化学结构是目标化学结构的超结构。
超结构相似性可以通过以下方式测量:
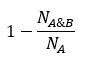
Superstructure.
其中
-
B是A的超结构
-
NA指定分子A指纹中的位数。
-
NB指定分子B指纹中的位数。
-
NAB指定分子A和B指纹中的共享位数。
Substructure
Substructure(子结构)用于衡量化学结构及其子结构之间的相似度。当值等于0时,这意味着数据库中的化学结构是目标化学结构的子结构。
子结构相似度可以通过以下方式进行衡量:
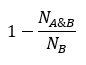
Substructure.
其中
-
B是A的子结构
-
NA指定了分子A指纹中的位数。
-
NB指定了分子B指纹中的位数。
-
NAB指定了分子A和B指纹共享的位数。
常见问题
Why is the top1 result of a vector search not the search vector itself, if the metric type is inner product? This occurs if you have not normalized the vectors when using inner product as the distance metric.
What is normalization? Why is normalization needed? 归一化指将嵌入(向量)转换为其范数等于1的过程。如果您使用内积计算嵌入相似性,则必须归一化您的嵌入。归一化后,内积等于余弦相似度。
更多信息请参见维基百科 (opens in a new tab)。
Why do I get different results using Euclidean distance (L2) and inner product (IP) as the distance metric? Check if the vectors are normalized. If not, you need to normalize the vectors first. Theoretically speaking, similarities worked out by L2 are different from similarities worked out by IP, if the vectors are not normalized.
What's next
- 了解 Milvus 中支持的索引类型。